Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
- Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):759-769. Published online October 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1515
- 3,182 View
- 192 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
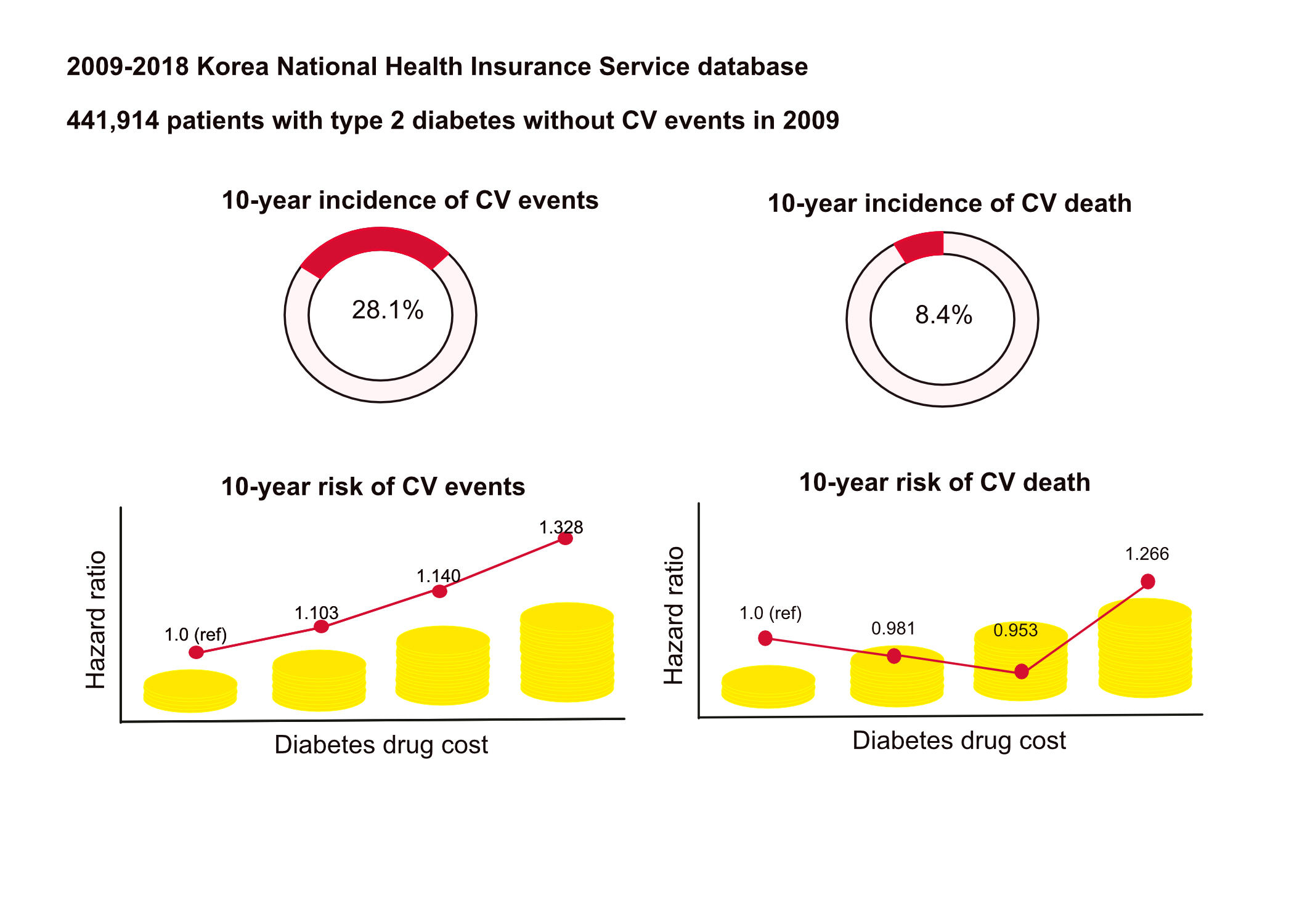
This study aimed to investigate the long-term effects of diabetes drug costs on cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
Methods
This retrospective observational study used data from 2009 to 2018 from the National Health Insurance in Korea. Among the patients with type 2 diabetes, those taking antidiabetic drugs and who did not have CV events until 2009 were included. Patients were divided into quartiles (Q1 [lowest]–4 [highest]) according to the 2009 diabetes drug cost. In addition, the 10-year incidences of CV events (non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, and coronary revascularization) and CV death (death due to CV events) were analyzed.
Results
A total of 441,914 participants were enrolled (median age, 60 years; men, 57%). CV events and death occurred in 28.1% and 8.36% of the patients, respectively. The 10-year incidences of CV events and deaths increased from Q1 to 4. After adjusting for sex, age, income, type of diabetes drugs, comorbidities, and smoking and drinking status, the risk of CV events significantly increased according to the sequential order of the cost quartiles. In contrast, the risk of CV death showed a U-shaped pattern, which was the lowest in Q3 (hazard ratio [HR], 0.953; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.913 to 0.995) and the highest in Q4 (HR, 1.266; 95% CI, 1.213 to 1.321).
Conclusion
Diabetes drug expenditure affects 10-year CV events and mortality. Therefore, affording an appropriate diabetes drug cost at a similar risk of CV is an independent protective factor against CV death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study

- Clinical Study
- A Novel Index Using Soluble CD36 Is Associated with the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Comparison Study with Triglyceride-Glucose Index
- Ho Jin Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Joong Hee Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(3):375-382. Published online September 18, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.3.375
- 4,649 View
- 47 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Plasma soluble cluster determinant 36 (sCD36) level is closely related with insulin resistance and atherosclerosis, but little is known whether it could be a surrogate for estimating risk of developing diabetes or not. To address this, we evaluated association between sCD36 index, the product of sCD36 and fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and then compared with triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index which has been suggested simple index for insulin resistance.
Methods This was cross-sectional study, and participants were classified as normal glucose tolerance (NGT), prediabetes, and T2DM according to glucose tolerance. The formula of TyG index was ‘ln [FPG (mg/dL)×triglyceride (mg/dL)/2],’ and the sCD36 index was ‘ln [sCD36 (pg/mL)×FPG (mg/dL)/2].’
Results One hundred and fifty-five subjects (mean age, 55.2 years) were enrolled, and patients with T2DM were 75. Both indexes were significantly increased in prediabetes and T2DM rather than NGT, and sCD36 index was positively correlated with both glycosylated hemoglobin and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (
r =0.767 andr =0.453, respectively;P <0.05) and negatively with homeostasis model assessment estimate of β-cell function (r =−0.317). The odds ratio (OR) of sCD36 index for T2DM was 4.39 (95% confidential interval, 1.51 to 12.77) after adjusting age, gender, blood pressure, smoking, alcohol, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. However, OR of TyG index did not remained significance after adjustment.Conclusion sCD36 index has an independent association with the risk of T2DM, and showed better correlation than TyG index. These results suggest sCD36 index might be useful surrogate marker for the risk of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The triglyceride-glucose index as an indicator of insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in Brazilian adolescents
Miriam Beatrís Reckziegel, Patrik Nepomuceno, Tania Machado, Jane Dagmar Pollo Renner, Hildegard Hedwig Pohl, Carlos Alberto Nogueira-de-Almeida, Elza Daniel de Mello
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of soluble cluster of differentiation 36 with metabolic diseases: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target
Yun Li, Yaxi Chen, Xiong Z. Ruan
Pediatric Discovery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2023; 19(10): 629. CrossRef - Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insulin resistance, lipid profile, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Martin-Yurii Markevich, Volodymyr Segin, Victoria Serhiyenko, Alexandr Serhiyenko
InterConf.2023; (35(163)): 213. CrossRef - Insulin resistance estimated by estimated glucose disposal rate predicts outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients
Zhengzhao Lu, Yunyun Xiong, Xueyan Feng, Kaixuan Yang, Hongqiu Gu, Xingquan Zhao, Xia Meng, Yongjun Wang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of SPISE Index for Screening and Detection of Early Stages of Insulin Resistance among Chilean Young Adults
Isabel Pereyra González, Sandra Lopez-Arana
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2023; 79(4): 372. CrossRef - Oxidative Stress Induced by Lipotoxicity and Renal Hypoxia in Diabetic Kidney Disease and Possible Therapeutic Interventions: Targeting the Lipid Metabolism and Hypoxia
Seung Yun Chae, Yaeni Kim, Cheol Whee Park
Antioxidants.2023; 12(12): 2083. CrossRef - Proteomic analysis of epicardial adipose tissue from heart disease patients with concomitant heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Shan He, Huagang Zhu, Jianjun Zhang, Xiaopeng Wu, Lei Zhao, Xinchun Yang
International Journal of Cardiology.2022; 362: 118. CrossRef - DIABETIC CARDIAC AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY: SIMVASTATIN, INSULIN RESISTANCE AND LIPIDS
Victoria Serhiyenko, Marta Hotsko, Samir Ajmi, Alexandr Serhiyenko
InterConf.2022; (18(95)): 531. CrossRef - New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, George Burke, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(5): 524. CrossRef - The Role of CD36 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: β-Cell Dysfunction and Beyond
Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Elumalai Suma, Seung Min Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 222. CrossRef - The Multifunctionality of CD36 in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications—Update in Pathogenesis, Treatment and Monitoring
Kamila Puchałowicz, Monika Ewa Rać
Cells.2020; 9(8): 1877. CrossRef
- The triglyceride-glucose index as an indicator of insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in Brazilian adolescents

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Variation in Serum Creatinine Level Is Correlated to Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- Jun Sung Moon, Ji Eun Lee, Ji Sung Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):207-213. Published online September 13, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.207
- 4,134 View
- 46 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Skeletal muscle is well established as a major target organ of insulin action, and is associated with the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Therefore, we attempted to determine whether a variation in serum creatinine is related to the development of type 2 diabetes and other risk factors for diabetes.
Methods A total of 2,676 nondiabetic subjects with stable and normal renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate >60 mL/min/1.73 m2) were followed up for approximately 4.5 years. New onset diabetes was defined as fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥7.0 mmol/L, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, or subjects taking antidiabetic agents. Variation of serum creatinine (ΔCre) was defined as a difference between follow-up and baseline creatinine. In subgroup analysis, body composition was examined by bioelectric impedance analysis method.
Results A total of 106 subjects were diagnosed with new-onset diabetes during the follow-up period. Baseline serum creatinine was not different between the new-onset diabetes and no diabetes groups. Negative ΔCre (ΔCre <0) showed an association with increased risk of type 2 diabetes after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, FPG, HbA1c, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (odds ratio, 1.885; 95% confidence interval, 1.127 to 3.153). Serum creatinine level demonstrated positive correlation with muscle mass and negative correlation with percentage of body fat in body composition analysis.
Conclusion Serum creatinine reflected body muscle mass and the decrease of serum creatinine might be regarded as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low serum creatinine, a surrogate marker of muscle mass, correlates with insulin sensitivity in nonhuman primates
Uddhav K. Chaudhari, Barbara C. Hansen
Journal of Medical Primatology.2023; 52(2): 100. CrossRef - Identification of Novel Biomarkers of Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Therapeutic Response by Proteomic and Metabolomic Profiling of Human Biological Fluid Samples
Megi Meneri, Elena Abati, Delia Gagliardi, Irene Faravelli, Valeria Parente, Antonia Ratti, Federico Verde, Nicola Ticozzi, Giacomo P. Comi, Linda Ottoboni, Stefania Corti
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1254. CrossRef - Association of serum creatinine levels and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea: a case control study
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Female Sex on the Susceptibility to Hypernatremia Among Older Community-Dwelling Individuals in Japan
Sho Tanaka, Midori Fujishiro, Kazuhiro Imatake, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Hisamitsu Ishihara, Shigemasa Tani
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 777. CrossRef - Ameliorative Effect of Oxytocin on FBN1 and PEPCK Gene Expression, and Behavioral Patterns in Rats' Obesity-Induced Diabetes
Asmaa Elnagar, Khalifa El-Dawy, Hussein I. El-Belbasi, Ibrahim F. Rehan, Hamdy Embark, Zeinab Al-Amgad, Obeid Shanab, Elsayed Mickdam, Gaber E. Batiha, Salman Alamery, Samer S. Fouad, Simona Cavalu, Mohammed Youssef
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Time to doubling of serum creatinine in patients with diabetes in Ethiopian University Hospital: Retrospective follow-up study
Adeladlew Kassie Netere, Ashenafi Kibret Sendekie, Donovan Anthony McGrowder
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0274495. CrossRef - Deep Learning for Integrated Analysis of Insulin Resistance with Multi-Omics Data
Eunchong Huang, Sarah Kim, TaeJin Ahn
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(2): 128. CrossRef - Arsenic Secondary Methylation Capacity Is Inversely Associated with Arsenic Exposure-Related Muscle Mass Reduction
Md. Khalequzzaman Sarker, Selim Reza Tony, Abu Eabrahim Siddique, Md. Rezaul Karim, Nazmul Haque, Zohurul Islam, Md. Shofikul Islam, Moriom Khatun, Jahidul Islam, Shakhawoat Hossain, Zahangir Alam Saud, Hideki Miyataka, Daigo Sumi, Aaron Barchowsky, Seiic
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9730. CrossRef - Creatinine to Body Weight Ratio Is Associated with Incident Diabetes: Population-Based Cohort Study
Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Takuro Okamura, Masahide Hamaguchi, Akihiro Obora, Takao Kojima, Michiaki Fukui
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 227. CrossRef - ¿Debemos prestar más atención a la creatinina baja?
Carlos A. Amado Diago, José A. Amado Señaris
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2020; 67(7): 486. CrossRef - Arsenic exposure-related hyperglycemia is linked to insulin resistance with concomitant reduction of skeletal muscle mass
Victor Mondal, Zubaer Hosen, Faruk Hossen, Abu Eabrahim Siddique, Selim Reza Tony, Zohurul Islam, Md. Shofikul Islam, Shakhawoat Hossain, Khairul Islam, Md. Khalequzzaman Sarker, M.M. Hasibuzzaman, Ling-Zhi Liu, Bing-Hua Jiang, Md Mominul Hoque, Zahangir
Environment International.2020; 143: 105890. CrossRef - Noninvasive assessment of abdominal adipose tissues and quantification of hepatic and pancreatic fat fractions in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Manoj Kumar Sarma, Andres Saucedo, Christine Hema Darwin, Ely Richard Felker, Kavya Umachandran, Daniel Kohanghadosh, Edward Xu, Steve Raman, Michael Albert Thomas
Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2020; 72: 95. CrossRef - Should we pay more attention to low creatinine levels?
Carlos A. Amado Diago, José A. Amado Señaris
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2020; 67(7): 486. CrossRef - Acute Effect of the Timing of Resistance Exercise and Nutrient Intake on Muscle Protein Breakdown
Wataru Kume, Jun Yasuda, Takeshi Hashimoto
Nutrients.2020; 12(4): 1177. CrossRef - Serum creatinine levels and risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus or dysglycemia in middle-aged Japanese men: a retrospective cohort study
Mamoru Takeuchi, Hironori Imano, Isao Muraki, Yuji Shimizu, Mina Hayama-Terada, Akihiko Kitamura, Takeo Okada, Masahiko Kiyama, Hiroyasu Iso
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2018; 6(1): e000492. CrossRef - Assessment of kidney dysfunction with cystatin C- and creatinine-based estimated glomerular filtration rate and predicting type 2 diabetes: Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 21
Yoriko Heianza, Shigeko Hara, Kazumi Saito, Hiroshi Tsuji, Shiro Tanaka, Satoru Kodama, Tetsuro Kobayashi, Yasuji Arase, Hirohito Sone
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 113: 60. CrossRef - Profiling human blood serum metabolites by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a comprehensive tool for the evaluation of hemodialysis efficiency
Marika Kromke, Martina Palomino-Schätzlein, Horst Mayer, Stefan Pfeffer, Antonio Pineda-Lucena, Burkhard Luy, Martin Hausberg, Claudia Muhle-Goll
Translational Research.2016; 171: 71. CrossRef - Safety evaluation of the consumption of high dose milk fat globule membrane in healthy adults: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial with parallel group design
Sayaka Hari, Ryuji Ochiai, Yasushi Shioya, Yoshihisa Katsuragi
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry.2015; 79(7): 1172. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Low serum creatinine, a surrogate marker of muscle mass, correlates with insulin sensitivity in nonhuman primates

- Ketoacidosis with Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Pancreatitis in a Patient with Gestational Diabetes: A Case Report.
- Hyun Hee Chung, Sang Hyun Park, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):89-92. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.89
- 2,071 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis in pregnancy is not a common complication. Moreover, ketoacidosis in gestational diabetes occurs rarely. Here we report a case of ketoacidosis with hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis in a patient with gestational diabetes that was successfully treated with insulin and supportive care. In this case, a 36-year-old woman (at 32 weeks' gestation) was diagnosed with gestational diabetes 4 weeks prior, but did not have well controlled blood sugar. She complained of severe epigastric pain concomitant with nausea and vomiting. Radiology and laboratory tests found hypertriglyceridemia (1,996 mg/dL), acute pancreatitis, and ketoacidosis with absence of fetal deceleration on a non-stress test. The patient's condition improved with insulin therapy and fluid replacement. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a case of ketoacidosis with hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis in a patient with gestational diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute Pancreatitis in a Pregnant Patient with Type IV Hyperlipoproteinemia
Sang Ho Lee, Jae Hyuck Jun, Young Seok Doh, Ji Woong Jang, Sae Hee Kim, Il Hyun Baek, Sung Hee Jung
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2019; 24(2): 73. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Acute Pancreatitis
Jin Myung Park
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2017; 22(4): 158. CrossRef - Cheese-like Material in the Heart: An Autopsy Case Report of Severe Hypertriglyceridemia in Diabetic Ketoacidosis Patient
Joo Young Na, Eun Hee Kim, Bon Young Koo, Ik Jo Chung, Byung Ha Choi, Nak Eun Chung
Korean Journal of Legal Medicine.2013; 37(4): 212. CrossRef
- Acute Pancreatitis in a Pregnant Patient with Type IV Hyperlipoproteinemia

- A Case of Panhypopituitarism with Rhabdomyolysis.
- Sung Wook Hong, Eun Jung Lee, Ji Young Park, Ji Sung Yoon, Ji O Mok, Yeo Joo Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Jae Woo Kim, Chul Hee Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Dong Won Byun, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(2):174-178. Published online April 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.2.174
- 1,500 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyolysis is the consequence of extensive muscle injury with the release of muscle cell constituents into plasma. It can arise from trauma and also from a variety of nontraumatic causes. Trauma, drugs, toxins and infection are the major causes of rhabdomyolysis, but it is rarely associated with metabolic disorders such as severe electrolyte disturbance, diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar nonketotic coma, hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. There have been several reported cases of metabolic rhabdomyolysis, but panhypopituitarism as a cause has never been identified. We experienced a case of acute rhabdomyolysis associated with panhypopituitarism. Thus, So we report this case with the review of related literature. Metabolic disorder is a rare cause of rhabdomyolysis, but it should always be considered in a patient having and unexplained increased of the creatine kinase concentration

- A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome with Unilateral Renal Aplasia and Diabetes Mellitus.
- En Jung Lee, Sung Wook Hong, Yun Ki Hong, Ji Sung Yoon, Ji O Mok, Yeo Joo Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Chul Hee Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Dong Won Byun, Won Kyung Bae, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(1):96-102. Published online February 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.1.96
- 2,067 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Kallmann's syndrome is defined as the combination of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia/hyposmia. The syndrome is a result of defect in the embryonic migratory pathway of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which synthesizes neurons and olfactory axons. The hypogonadotropic hypogonadism results due to absence of or incomplete pubertal development and may be associated with anosmia, hyposmia, midline defect(color blindness, cleft-lip, cleft-palate, unilateral renal agenesis, sensorineural deafness), cryptorchidism and skeletal anomaly. Till date in Korea, few cases of Kallmann's syndrome have been reported but there are no available reports on cases of Kallmann's syndrome with unilateral renal aplasia and diabetes mellitus. We handled a case of Kallmann's syndrome associated with unilateral renal agenesis and diabetes mellitus. In the current work, we present a peculiar case as afore mentioned with the review of related literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome with Frontal Lobe Atrophy and Mental Retardation
Soyoung Hyun, Seungguk Park, Dong Gu Kang, Seung Uk Jeong, Dea Ho Lee, Gwanpyo Koh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2010; 25(2): 142. CrossRef - A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome Mildly Presenting as Secondary Amenorrhea
Na Rae Joo, Cheol Young Park, Hong Ju Moon, Jun Goo Kang, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Yul Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung woo Park
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2007; 22(2): 130. CrossRef
- A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome with Frontal Lobe Atrophy and Mental Retardation

- A Case of Thyrotoxic Paraplegia.
- Gun Wha Lee, Jin Woo Park, Ji Sung Yoon, Ji O Mok, Yeo Joo Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Chul Hee Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Dong Won Byun, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo, Du Shin Jeong
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(4):419-425. Published online August 1, 2004
- 1,079 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyperthyroidism may be associated or present with a variety of neuromuscular disorders, including thyrotoxic myopathy, exophthalmic ophthalmoplegia, periodic paralysis and myasthenia gravis. In contrast to muscle, peripheral nerve involvement in hyperthyroidism is exceedingly rare, and has received little attention. Paraplegia-like weakness during severe hyperthyroidism was first described by Charcot in 1889, and called Basedow's paraplegia' by Joffory in 1894. However, there has been no reported case in Korea. A 38-year-old woman was admitted for evaluation of progressive weakness and a gait disturbance. Her endocrinological results were compatible with hyperthyroidism. The polyneuropathy was also confirmed with sequential electrophysiological studies of the nerves and muscles. Drug therapy for hyperthyroidism resulted in resolution of the clinical neurological symptoms and progressive improvement of electrophysiological findings. Hyperthyroidisms are common medical disorders, which are often accompanied by diverse types of neurological and neuromuscular dysfunctions. All of these neurological manifestations are important, as they can serve as important clues to the diagnosis of a thyroid disorder. Furthermore, they are often related to the patient's presenting complaint. Therefore, the physician must be alert to the diverse manifestations of thyroid dysfunction, as they can lead to the diagnosis of potentially serious but treatable disorders. Herein is reported a case of myopathy and neuropathy associated with hyperthyroidism (Basedow's paraplegia), with a review of the literature

- Increased Activity of Insulin-like Growth Factor binding Protein-4 Protease in H-mole Patients.
- Woo Seok Seo, Dong Won Byun, Ji Oh Mok, Ji Sung Yoon, Yeo Joo Kim, Hyung Kyu Park, Chul Hee Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo, Hae Hyeog Lee, Soo Kyoon Rah
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(4):346-357. Published online August 1, 2004
- 1,112 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Hydatidiform mole (H-mole) is characterized by the neoplastic proliferation of trophoblasts. Only 1~10% of patients with partial H-mole will develop a trophoblastic tumor, but 18~29% of those with complete H-mole will develop a persistent trophoblastic tumor. Therefore, the early diagnosis and monitoring after operation of an H-mole disease are very important. Recently, the pregnancy associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) was proved to have a similar role as that of IGF binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) protease, which has shown an increasing function in fetal growth and development by degradation of IGFBP-4 and an increase in IGF in the serum during pregnancy. Our hypothesis is "the H-mole, which shows placental hyperplasia will also have an IGFBP-4 protease activity, which may be used as in the early diagnosis and monitoring of H-mole disease". METHODS: Serum samples from 6 non-pregnant, 18 pregnant (5 in the 1st trimester, 10 in the 2nd, and 3 in the 3rd), 12 postpartum women and 3 H-mole patients(2 with complete H-mole and 1with partial H-mole) were collected and measured for the -HCG, IGF and PAPP-A levels and IGFBP-4 protease activities by a IGF-II ligand blot analysis and electrophoresis method. The IGFBP-4 protease activity of the serum during normal pregnancy was compared with that of H-mole disease. RESULTS: The results from the in vitro protease assays using recombinant IGFBP-4 determined that IGFBP-4 proteolysis was significantly increased during the first (56%) and second trimesters (90%), but reached a plateau by the third trimester (94%). In H-mole disease diagnosed 11 weeks after conception, the IGFBP-4 proteolytic activity was 97%, which was nearly the same as at terminal pregnancy. This activity gradually decreased to 75% at 1 week, 58.7% at 2 and 33% at 3 weeks after the operation. The -HCG was also decreased from 490,400 to 123,822.7, 1,352.3, and 128.5 mIU/mL at 1, 2 and 3 weeks after the operation, respectively. The PAPP-A level also gradually decreased from 34.87 to 25.5, 12.0 and 2.7 g/mL 1, 2 and 3 weeks after the operation, respectively. However, the IGF decreased from 238.3 to 172.9 ng/mL 1 week after the operation, but increased to 251.4 and 295 ng/mL at 2 and 3 weeks after the operation, respectively. CONCLUSION: These results demonstrated that the IGFBP-4 protease activity was significantly increased during pregnancy, and was extremely elevated durimg the early stages of H-mole disease, but gradually decreased after removal of molar tissue. Therefore, measuring the IGFBP-4 protease activity may play an important role in the early diagnosis and monitoring of H-mole disease

- A Case of Severe Thyrotoxicosis Induced by Hydatidiform Mole.
- Jae Hak Lee, Jong Kun Park, Soon Hyo Kwon, Ji Oh Mok, Ji Sung Yoon, Yeo Joo Kim, Hyung Kyu Park, Chul Hee Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Hae Hyeog Lee, Gye Hyun Nam, Gye Hyun Kwan, Eun Suk Ko, Dong Won Byun, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(4):420-425. Published online August 1, 2003
- 1,179 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is one of the glycoproteins families synthesized by the placenta, and consists of 2 noncovalently joined subunits, namely, alpha and beta. The alpha and beta-subunits have a structural homology with the alpha and beta-subunits of TSH and LH. The thyrotropic action of HCG results from its structural similarity to TSH, so beta-HCG can bind to the TSH receptor in the thyroid gland. A high level of HCG, accompanied by an increased thyroid hormone level, can be observed in gestational trophoblastic diseases (GTD), such as a hydatidiform mole or a choriocarcinoma. However, the clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism in GTD are rarely observed. A 27-years-old woman, admitted due to an amenorrhea of 11 weeks duration, with thyrotoxic symptoms, such as weight loss, palpitation, sweating, tremor, heat intolerance and anxiety, was evaluated. Her serum free T4 level was 8 times higher than normal, and her serum beta-HCG level was over 1,000,000IU/L. She had a curettage operation, with the pathological findings of a complete hydatidiform mole. These thyrotoxic symptoms developed due to a hydatidiform mole, and were accompanied with a highly increased serum beta-HCG level. After evacuation of the molar tissue, the thyroid hormone and thyrotoxic symptoms normalized. Here, this case is reported, with brief review of the literature.

- Evaluation of Lung Epithelial Permeability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus using 99mTc-DTPA Aerosol Scintigraphy.
- Ji Sung Yoon, Mi Jung Eun, Si Hyung Lee, Jae Hong Kim, Young Hoon Hong, Kyu Chang Won, Ihn Ho Cho, Hyoung Woo Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(2):246-256. Published online April 1, 2002
- 1,070 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diabetes mellitus is often accompanied by complicated microangiopathy, such as, retinopathy, nephropathy, peripheral neuropathy, cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy or macroangiopathy, as well as by coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease. However, there have been few reports concerning the pulmonary involvement of diabetes. Recently, capillary basement membrane thickening, nonenzymatic glycosylation of tissue proteins, abnormalities of endothelial cells and increased damage by free radicals were reported as the underlying basis for the reduced lung permeability. 99mTc-DTPA aerosol scintigraphy is a noninvasive, accurate method, which evaluates the permeability of lung epithelial membranes. The clearance rate of 99mTc-DTPA in lungs may correlate inversely with the lung's epithelial permeability. We investigated the relationship between microangiopathies and the lung epithelial permeability in patients with diabetes using 99mTc-DTPA aerosol scintigraphy. METHODS: The study group comprised of 33 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with no clinical evidence of past or present respiratory disease. The patients were divided into two groups in relation to the complications. Group 1: 16 patients with more than one of the complications of retinopathy, nephropathy, cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and/or peripheral neuropathy, and comprised of 3 males and 13 females, with a mean age of 52.9 +/- 9.6 years. Group 2: 17 patients with no complications, and comprised of 5 males and 12 females with a mean age of 52.8 +/- 11.5 years. Group 3: as a control group, comprised of 11 healthy people: 4 males 4 and 7 females with a mean age of 44.2 +/- 12.5 years. 99m-Tc-DTPA aerosol scintigraphy was performed in the subjects by inhalation of 30 mCi 99mTc-DTPA aerosol and oxygen (9 l/min) using an aero-vent jet nebulizer as the lung delivery system. To evaluate the diabetic complications, CAN (Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy), and NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity) tests for peripheral neuropathy, fundoscopy for retinopathy and 24 hours urine microalbumin for nephropathy were performed. RESULTS: The mean durations of diabetes in Groups 1 and 2 were 11.1 +/- 4.7 years and 3.8 +/- 2.1 years, respectively (p<0.05). The mean clearance rates of 99mTc-DTPA were found to be 72.1 +/- 19.5min, 52.6 +/- 19.7 min, and 47.1 +/- 10.9 min for Groups 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The mean clearance rate of Group 1 was significantly longer than for Groups 2 and 3 (p<0.05). In other words, the pulmonary epithelial permeability was reduced in diabetic patients with complications compared to the patients without complication and/or the normal controls. Significant positive correlation was found between the pulmonary clearance rate of 99mTc-DTPA, and peripheral neuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (p<0.05). Conclusions: The lungs may be a target organ for diabetes, and impaired pulmonary epithelial permeability seems to be closely related to other diabetic microangiopathies. Therefore, we recommend that 99mTc-DTPA aerosol scintigraphy be used as a technique for assessing lung injury in diabetic patients.

- Clinical Features of Ectopic Thyroid Gland.
- Jin Chul Park, Jung Hyun Oh, Sang Yub Nam, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Jang Won, In Ho Cho, Hyung Woo Lee, Choong Ki Lee, Jae Tae Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(4):563-571. Published online January 1, 2001
- 940 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Ectopic thyroid gland is relatively rare condition and a developmental anomaly characterized by an aggregated of thyroid tissue in the midline anywhere from the base of the tongue to the mediastinum. The role of ectopic thyroid in the pathogenesis of non-goitrous sporadic cretinism and primary hypothyroidism has been emphasized. 19 cases of ectopic thyroid for 12 years was presented with Tc-pertechnetate or radioactive iodine, which were diagnosed by scintigraphy. METHODS: We wish to report these 19 cases and 12 cases of brief review of literatures on the incidence, etiology and development, symptomatology, diagnosis and treatment of ectopic thyroid gland was done. RESULTS: The most frequent incidental age was between the age 1 year and 29 years. And the frequency of ectopic thyroid was about 7 times more common in female(27 cases) than in male(4 cases). The location of ectopic thyroid were found to be lingual in 18 cases, sublingual in 9 cases, prelaryngeal in 1 case, and combine with lingual and sublingual in 3 cases. In chief complaints, palpable mass was most common and there were foreign body sensation on throat, dysphagia, dysphonia, and hoarseness. In 15 cases of hypothyroidism, l2 cases were taken thyroid hormone replacement therapy, 1 case was removed ectopic thyroid gland. In 2 of 10 cases of euthyroidism, replacement of thyroid hormone were done and 2 cases were removed ectopic thyroid gland, in 6 cases of unknown thyroid function, 1 case was removed ectopic thyroid gland and 131I therapy was done in 1 case, and others were observed with following up thyroid function test. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the long terms thyroid function test, thyroglossal duct eyst and malignant change in ectopic thyroid tissue when finding the ectopic thyroid in thyroid scintigraphy were recommended highly.

- Comparison of Double Phase 99mTc-sestamibi Scintigraphy with Evaluation of Hyperparathyroidism.
- Jin Chul Park, Jung Hyun Oh, Sang Yub Nam, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Jang Won, In Ho Cho, Hyung Woo Lee, Jae Tae Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(3):384-393. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,060 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - "BACKGROUND: Between 80 to 85% of patients with hyperparathyroidsm have a solitary adenoma of the parathyroid glands and another 15% have a parathyroid hyperplasia. Preoperative localization of the parathyoid glands is generally accepted as warranted in patients who have failed an initial attempt at parathyroidectomy, ectopic locations and inexperienced surgeons. Different imaging techniques have been used for detection of abnormal parathyroid glands such as high resolution ultrasonography, computerized tomography, arteriography, venous sampling or magnetic resonance imaging and 201Tl/99mTc subtraction scintigraphy. But these methods have had varying rates of success, with low specificity and low sensitivity. Among the several different techniques available for parathyroid radionuclide imaging, the most common is the use of a dualradioisotope procedure combining of Tl with Tc. However, there are some controversies regarding the optimal technical aspects of this procedure, including the relative amount of injected dose of radiotracers, failed detection for small sized and deeper cervical located parathyroids, and not easy procedures. Recently, double phase Tc-sestamibi scintigraphy would be useful to solve these technical limitations, more convenient and have higher sensitivities. The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-sestamibi with 201Tl/ 99mTc subtraction scintigraphy in the localization of hyperparathyroidism. METHODS: 9 patients with hyperparathyroidism underwent preoperative evaluation with double phase 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy and 201Tl/99mTc subtraction scintigraphy for attempted localization of abnormal parathyroid glands and surgical explorations. Imaging results were compared to surgical findings. RESULTS: Of 9 patients, 7 had a solitary parathyroid adenoma, 1 had a carcinoma and 1 had parathyroid hyperplasia. The 201Tl/99mTc subtraction scintigraphy preoperatively localized 8 of 9 patients(sensitivity: S9%) and 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy correctly localized all lesions for a sensitivity of 100%. In one case, 201Tl/99mTc subtraction scan show only a hot uptake at left upper parathyroid area, but 99mTc-sestamibi scan was shown the three site of hot uptake at left upper, both inferior parathyroid area. CONCLUSION: In patients with hyperparathyoridism, 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy may be used as the single imaging technique as it show a very high sensitivity and specificity in the preoperative localization of pathological parathyroid glands.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



